Alzheimer’s early detection is a critical frontier in the fight against cognitive decline, as identifying this devastating disease in its infancy can significantly alter patient outcomes. Recent research has unveiled innovative methods, like home tests for Alzheimer’s, utilizing olfactory testing to determine an individual’s olfactory discrimination capabilities. Such tests allow participants to engage in simple scent identification tasks, revealing early signs of Alzheimer’s before even noticeable memory loss occurs. This breakthrough holds promise for millions at risk, providing a proactive approach to Alzheimer’s test development that can potentially lead to timely interventions. As experts emphasize, recognizing cognitive impairment early may not only enhance individual quality of life but also change the trajectory of Alzheimer’s treatments overall.
The quest for identifying potential neurodegenerative diseases has taken a groundbreaking turn with advances in cognitive health assessments. Utilizing novel at-home assessments, researchers are now exploring how diminished smell perception can signal underlying risks, particularly linked to conditions like Alzheimer’s. These olfactory tests are designed to help detect early indicators of cognitive decline, enabling timely medical attention for those who might be facing future memory challenges. By integrating these innovative home tests, individuals and healthcare providers can better manage cognitive health and potentially stave off severe symptoms as they arise. The focus on early intervention is essential, making these tests a game-changer in the realm of Alzheimer’s awareness and prevention.
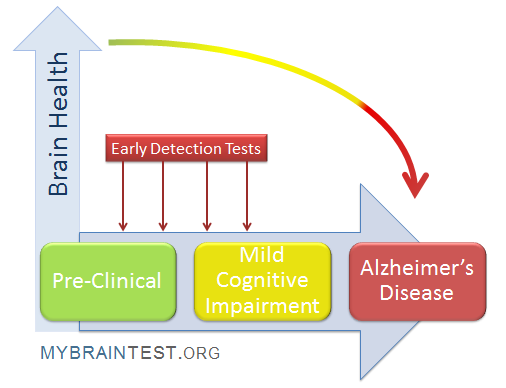
The Importance of Alzheimer’s Early Detection
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease is crucial for improving patient outcomes. Identifying symptoms before they progress allows for timely interventions that can slow the trajectory of cognitive decline. Recognizing early signs of Alzheimer’s can also provide patients and families with time to plan and prepare for future changes. As researchers emphasize, detecting cognitive impairment early opens avenues for implementing treatment strategies that may enhance the quality of life for individuals at risk.
Moreover, Alzheimer’s early detection can significantly reduce healthcare costs over time. Preventative measures and early treatment can alleviate the burden on caregivers and health systems by potentially delaying the advanced stages of the disease. With innovations in Alzheimer’s testing, such as olfactory assessments, we now have the tools necessary to identify cognitive impairment years before significant symptoms arise.
Understanding Olfactory Testing and Its Role in Alzheimer’s Screening
Olfactory testing is a groundbreaking method that researchers believe could revolutionize the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Conducted as a simple home test, it assesses an individual’s ability to smell and process odors, which can be an indicator of cognitive health. Studies have indicated that a decline in the ability to identify and discriminate odors may correlate with early cognitive impairment, making this a valuable tool in at-home Alzheimer’s testing.
Administering olfactory tests remotely has proved effective, enabling a more accessible method for monitoring cognitive function among older adults. The simplicity of the home test not only facilitates ease of use for patients but also broadens the participant pool for research. With preliminary findings suggesting lower olfactory scores in older adults with cognitive impairment, olfactory testing may soon be a standard component of Alzheimer’s screening protocols.
Recognizing the Early Signs of Alzheimer’s Disease
Recognizing the early signs of Alzheimer’s disease is essential for enabling effective intervention. Symptoms such as memory loss, confusion with time or place, and difficulty completing familiar tasks may start subtly in some individuals. Researchers and healthcare providers stress that family members should be vigilant for changes in behavior or cognition. Early recognition can prompt individuals to seek testing, which could confirm or rule out cognitive impairment.
Additionally, educating the public on cognitive health and potential warning signs is vital. Community resources and healthcare providers must work together to increase awareness and facilitate early Alzheimer’s tests. By doing so, we can empower individuals to take proactive steps in monitoring their cognitive health, allowing for earlier diagnosis and treatment options.
Home Testing for Alzheimer’s: A New Frontier
The advent of home testing for Alzheimer’s marks a significant breakthrough in the field of cognitive health. Home tests offer the convenience of assessing cognitive function in a familiar environment, promoting ease and comfort for older adults. These tests, particularly olfactory assessments, can detect early signs of Alzheimer’s and allow for quicker responses to cognitive decline.
As technology and research advance, the potential for home tests to be integrated into routine health assessments grows. By making Alzheimer’s testing accessible and straightforward, it’s possible to increase early detection and improve the trajectory of care. This shift in approach could fundamentally change how we address Alzheimer’s disease, allowing for more timely interventions.
Advancements in Alzheimer’s Testing Technology
Recent advancements in Alzheimer’s testing technology underscore the importance of innovative methodologies in cognitive health research. Olfactory testing has emerged as a promising tool for detecting early cognitive impairment and may become a standard practice in assessing Alzheimer’s risk. This non-invasive approach allows for easy administration and interpretation, both in clinical settings and within patients’ homes.
The Aromha Brain Health Test, a product of ongoing research, illustrates how technology can facilitate early detection. Continuous advancements are likely to result in more comprehensive tools that combine multiple assessments of cognitive function—beyond just olfactory tests—to create a more rounded view of an individual’s cognitive health.
Neuropsychological Tests: Complementing Olfactory Assessments
While olfactory tests provide critical insights into cognitive health, they should be complemented with neuropsychological evaluations for a comprehensive understanding. These traditional assessments help to gauge various cognitive functions, including memory, attention, and executive function. When used together with olfactory testing, healthcare professionals can paint a fuller picture of an individual’s mental acuity.
Implementing a dual approach allows for better screening and may pinpoint specific cognitive deficits linked to Alzheimer’s. This combination of tests enhances the reliability of early Alzheimer’s diagnosis, improving the chances for timely intervention and ultimately improving patient care.
The Role of Family and Caregivers in Alzheimer’s Awareness
Family members and caregivers play a pivotal role in recognizing Alzheimer’s risk factors and supporting individuals in seeking early detection. Educating families on the importance of monitoring cognitive health is essential. They can assist in prompting loved ones to engage in Alzheimer’s testing if they notice early signs of cognitive impairment.
Empowered with knowledge, caregivers can also advocate for access to resources and testing opportunities. By fostering an environment of awareness and proactivity, families can significantly impact the early detection process, facilitating timely interventions that can enhance the quality of care.
Cognitive Impairment: A Growing Concern Among Older Adults
Cognitive impairment is becoming increasingly prevalent as the population ages, making awareness and early detection more critical than ever. Conditions like Alzheimer’s not only affect the individual but also place a strain on caregivers and the healthcare system. As we understand more about cognitive health, particularly through innovative testing methods like olfactory assessments, the focus must shift toward proactive measures.
Addressing cognitive impairment requires a multifaceted approach—community education, effective screening tools, and accessible resources—aimed at promoting early detection. By emphasizing the importance of cognitive health, we can better prepare society to manage and mitigate the impacts of Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Future Implications of Alzheimer’s Testing Research
Research into Alzheimer’s testing techniques, such as olfactory assessments, has significant future implications for screening and early detection practices. Continued studies may pave the way for integrating these innovative testing methods into standard clinical practices, allowing healthcare providers to identify cognitive impairments earlier and more accurately.
As additional research emerges, we could see expanded applications, such as the development of automated home testing devices that incorporate multiple aspects of cognitive function. Such advancements would not only enhance the detection of Alzheimer’s but could also broaden understanding of its pathophysiology, ultimately helping to better address its impact on individuals and society.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of Alzheimer’s early detection through olfactory testing?
Alzheimer’s early detection through olfactory testing is significant because it allows for the identification of individuals at risk of cognitive impairment before symptoms arise. Studies show that a simple test, which involves distinguishing odors, can indicate potential neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s. Early intervention can lead to better management of the disease.
How can an at-home test for Alzheimer’s help with early detection?
An at-home test for Alzheimer’s can facilitate early detection by providing a cost-effective, noninvasive method to assess cognitive function and olfactory discrimination. This allows individuals to easily monitor changes in their sense of smell, which research suggests may be an early sign of Alzheimer’s.
What are some early signs of Alzheimer’s disease that can be detected through testing?
Some early signs of Alzheimer’s disease that can be detected through testing include difficulty in odor identification, memory loss, and a decline in cognitive functions. Research has indicated that individuals with mild cognitive impairment often score lower on olfactory tests, suggesting a link between sense of smell and early Alzheimer’s detection.
Why is olfactory testing important for Alzheimer’s cognitive impairment assessment?
Olfactory testing is important for Alzheimer’s cognitive impairment assessment because it can highlight subtle declines in scent recognition and memory that may indicate early neurodegenerative changes. This type of testing has been shown to differentiate between cognitively normal individuals and those experiencing early signs of Alzheimer’s, paving the way for timely interventions.
Can Alzheimer’s tests predict the onset of cognitive decline?
Yes, Alzheimer’s tests, particularly those focused on olfactory function, can predict the onset of cognitive decline. Research indicates that individuals with lower scores on odor discrimination tests are more likely to develop Alzheimer’s or other cognitive impairments over time, making early detection efforts critical for future interventions.
What types of home tests are available for Alzheimer’s early detection?
Home tests for Alzheimer’s early detection primarily include olfactory testing kits that assess the ability to identify and remember different smells. These simple tests can provide valuable insights into an individual’s cognitive health and potential risk factors associated with Alzheimer’s.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Research Overview | Researchers from Mass General Brigham have developed a home test for early detection of Alzheimer’s risk. |
| Olfactory Testing | Participants identified and remembered odors through a card test, scoring lower in cognitively impaired adults. |
| Significance | The study indicates that olfactory dysfunction can be an early warning sign for Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases. |
| Dual Language Testing | Successful outcomes for both English- and Spanish-speaking participants were observed. |
| Future Directions | Further studies may include neuropsychological assessments over time to evaluate predictive capabilities. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s early detection is crucial in identifying individuals at risk before symptoms manifest. The latest research indicates that a simple olfactory test conducted at home can significantly aid in this process. By detecting changes in the ability to identify and remember odors, clinicians may identify cognitive decline linked to Alzheimer’s disease years ahead of typical symptoms. This innovative approach could revolutionize Alzheimer’s research, paving the way for timely interventions and improved patient outcomes.