Age-related brain diseases pose a significant challenge to health and well-being, particularly as the population ages. Conditions such as stroke, dementia, and late-life depression are deeply interconnected, often sharing modifiable risk factors that can be addressed through preventative health strategies. Recent research indicates that altering just one of the identified risk factors can significantly lower the incidence of these conditions, raising awareness for effective stroke prevention and dementia risk reduction methods. Maintaining brain health becomes crucial not only for enhancing quality of life but also for averting serious health issues. By understanding and managing the modifiable risk factors linked to these diseases, we empower ourselves to take control of our cognitive futures and mitigate the detrimental impacts of age-related brain diseases.
The landscape of cognitive health is increasingly scrutinized as researchers uncover the complexities behind age-related neurologic disorders. These disorders, often referred to as cognitive decline or neurodegenerative conditions, can manifest as strokes, memory impairment, and emotional challenges like late-life depression. As we age, the risk intensifies for various health complications, making it essential to explore the underlying factors contributing to these diseases. Recognizing the significance of preventive measures is vital in safeguarding brain vitality, and engaging with lifestyle changes can help reduce the chances of developing these debilitating conditions. By approaching brain health holistically, individuals can adopt strategies that not only target specific risk factors but also foster long-term mental wellness.
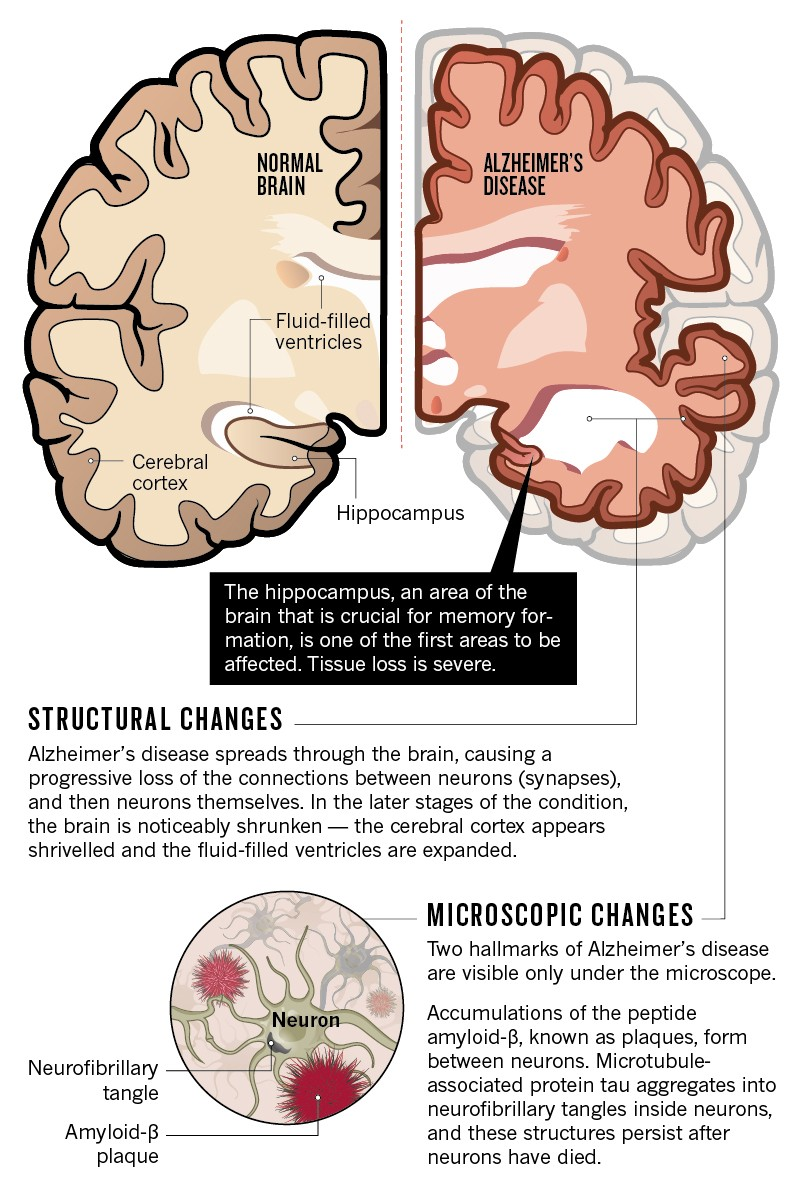
Understanding Age-Related Brain Diseases
Age-related brain diseases, including stroke, dementia, and depression, pose significant health challenges as the population ages. These conditions are interconnected, often sharing common risk factors that can amplify their effects. For instance, a stroke can lead to complications such as cognitive decline, which can further increase the likelihood of developing dementia. Similarly, untreated depression may exacerbate brain health issues, creating a vicious cycle that affects quality of life. Understanding these diseases is essential for developing effective preventive measures.
Research into age-related brain diseases has revealed that the risk factors associated with these conditions are not fixed; many are modifiable through lifestyle changes. High blood pressure, diabetes, and smoking are critical contributors to the onset of these diseases. By identifying and modifying these risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their brain health and reduce their risk of experiencing such debilitating conditions.
The Impact of Modifiable Risk Factors on Brain Health
Modifiable risk factors play a crucial role in lowering the incidence of age-related brain diseases. According to recent studies, including one conducted by researchers at Mass General Brigham, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of conditions like stroke and dementia by targeting modifiable factors. These factors include maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol use. Each of these lifestyle choices contributes to overall brain health, making it imperative for individuals to focus on these areas.
Moreover, the study highlighted the importance of social engagement and having a sense of purpose in life as protective factors against the development of depression and cognitive decline. Engaging in meaningful social interactions and activities can not only improve mental health but also provide a buffer against age-related cognitive decline. Therefore, implementing preventive health strategies that encompass a broad range of lifestyle modifications can yield significant benefits for maintaining brain health throughout aging.
Stroke Prevention: Key Strategies for Reducing Risk
Stroke prevention is critical in reducing the incidence of age-related neurological disorders. The identification of risk factors shared by stroke and other brain diseases allows for targeted prevention strategies. For instance, controlling high blood pressure through diet, exercise, and medications can lower the risk of stroke significantly. Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels and blood sugar can further assist individuals in taking early preventive measures.
In addition, lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption are proven methods to minimize stroke risk. Educational initiatives focusing on these modifiable risk factors can empower individuals to make informed health choices, effectively decreasing the prevalence of strokes in the population. As these prevention strategies become more widely adopted, the long-term benefits for society, including reduced healthcare costs and improved quality of life, will become evident.
Dementia Risk Reduction Through Lifestyle Changes
Dementia remains one of the most challenging age-related brain diseases, affecting millions of individuals worldwide. However, recent research indicates that addressing certain modifiable risk factors can substantially reduce the risk of developing dementia. For instance, engaging in regular physical exercise not only supports physical health but also enhances cognitive function, reducing the likelihood of dementia onset. Mental stimulation through activities like reading or puzzles can also contribute significantly to brain health.
Additionally, maintaining a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids is linked with lower dementia risk. Nutrition impacts overall brain health profoundly. A diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients that support cognitive function. By employing these preventive health strategies, individuals can lower their risk of dementia effectively, emphasizing the importance of lifestyle choices in overall brain health.
The Role of Depression in Age-Related Brain Diseases
Depression is often overlooked in discussions of age-related brain diseases, yet it is a significant risk factor that can exacerbate conditions such as stroke and dementia. The relationship between depression and cognitive decline is complex, as depression can impair cognitive functions, leading to an increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Recognizing depression as a critical modifiable risk factor highlights the importance of mental health care for older adults.
Moreover, early intervention strategies for managing depression can have a profound impact on reducing overall mortality and improving quality of life. Treating depression effectively not only alleviates mental suffering but may also protect against cognitive decline, illustrating how interconnected our mental and physical health truly is. This underscores the necessity of comprehensive health assessments that consider psychological well-being as part of preventive health strategies.
Implementing Preventive Health Strategies for Brain Care
Implementing preventive health strategies is essential for managing age-related brain diseases. The introduction of tools like the Brain Care Score offers individuals a structured approach to evaluate their brain health. By focusing on the identified modifiable risks, such as sleep quality, social engagement, and overall nutrition, individuals can make informed adjustments to their lifestyle that promote cognitive longevity.
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in guiding patients through these preventive measures. Educating patients about the significance of lifestyle changes, encouraging regular check-ups, and fostering supportive environments for mental health are key components in the fight against brain diseases. As research continues to evolve, staying abreast of new findings regarding brain health will be crucial for both patients and healthcare providers.
Social Engagement: Its Importance in Brain Health
Social engagement has emerged as a critical protective factor against the decline in brain health associated with aging. Studies have shown that individuals who maintain active social networks and engage in community activities tend to experience lower rates of dementia and depression. This is primarily because social interaction stimulates cognitive functions and provides emotional support, which is essential for mental wellness.
Moreover, fostering social connections helps reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation, which are known contributors to cognitive decline and mental health issues. Creating opportunities for social interaction—be it through clubs, volunteer work, or regular gatherings—underscores the importance of a community-focused approach to health. Thus, promoting social engagement is not just beneficial but essential for enhancing brain health and reducing the risks associated with age-related brain diseases.
Dietary Choices and Brain Health: What to Know
Dietary choices play a pivotal role in supporting brain health and can significantly influence the risk of age-related brain diseases. A diet rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals supports cognitive function and overall brain resilience. Foods such as leafy greens, fatty fish, and berries have been linked to lower rates of cognitive decline, illustrating the profound impact of nutrition on brain health.
In addition, maintaining a balanced and nutrient-dense diet can help manage other modifiable risk factors such as obesity, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar. By making informed dietary choices and adopting a whole-foods approach, individuals can not only improve their physical health but also reduce their risk of developing conditions like stroke and dementia. As awareness about the relationship between diet and brain health grows, individuals are encouraged to prioritize nutrition as a fundamental aspect of their overall health strategy.
Physical Activity: A Cornerstone of Brain Care
Physical activity is a cornerstone of brain care and has been shown to have numerous benefits for cognitive health. Regular exercise increases blood flow to the brain, promoting the growth of new brain cells and enhancing mental function. Engaging in physical activities, whether through structured workouts or everyday tasks, can reduce the risk of stroke and dementia significantly.
Incorporating exercise into daily routines does not have to be overwhelming. Simple changes like walking, dancing, or even gardening can contribute to maintaining an active lifestyle. By prioritizing physical activity, individuals can leverage its protective effects on brain health, reinforcing the idea that even small, consistent efforts can lead to substantial long-term benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are modifiable risk factors associated with age-related brain diseases?
Modifiable risk factors related to age-related brain diseases include high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, kidney disease, and lifestyle factors such as diet, physical activity, and smoking. By addressing these factors, individuals can lower their risk of developing conditions like stroke, dementia, and late-life depression.
How can lifestyle changes reduce dementia risk in older adults?
Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels can significantly reduce dementia risk. Engaging in social activities and having a purpose in life also contribute to better brain health, ultimately minimizing the risk of age-related brain diseases.
What is the connection between stroke prevention and age-related brain diseases?
Stroke prevention is crucial as it not only helps avoid immediate health crises but also lowers the risk of subsequent conditions, such as dementia and depression, which are interrelated with stroke. Addressing key modifiable risk factors can create a ripple effect in lowering the incidence of these age-related brain diseases.
What are some preventive health strategies for brain health?
Preventive health strategies for brain health include managing chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension, engaging in regular physical activity, eating a balanced diet, avoiding smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and ensuring proper sleep. These practices are effective in reducing the risk of age-related brain diseases.
How does depression relate to other age-related brain diseases?
Depression can increase the risk of developing other age-related brain diseases such as dementia and stroke. It is imperative to address mental health concerns as part of a holistic approach to brain health and disease prevention, considering shared modifiable risk factors among these conditions.
What role does social engagement play in preventing age-related brain diseases?
Social engagement is a significant modifiable risk factor for age-related brain diseases. Maintaining strong social connections can help decrease depression and enhance cognitive function, contributing to a lower risk of dementia and stroke in older adults.
How effective is the Brain Care Score in promoting brain health?
The Brain Care Score is an effective tool developed to assess and promote brain health by evaluating lifestyle habits and risk factors. By improving scores through targeted lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of age-related brain diseases.
Which dietary habits are associated with lower dementia risk?
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is associated with lower dementia risk. Avoiding excessive sugars, unhealthy fats, and processed foods also plays a critical role in maintaining overall brain health and reducing the incidence of age-related brain diseases.
Can managing sleep patterns help reduce the risk of dementia?
Yes, managing sleep patterns is vital for reducing the risk of dementia. Poor sleep quality and quantity can lead to cognitive decline and is linked to higher rates of age-related brain diseases, making sufficient rest a key component in brain health strategies.
What impact does high blood pressure have on brain health in aging individuals?
High blood pressure is a significant modifiable risk factor that can increase the risk of stroke, dementia, and late-life depression. Controlling blood pressure through healthy lifestyle changes and medical interventions is essential for preserving brain health as individuals age.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Research Study | Identified 17 modifiable risk factors for age-related brain diseases. |
| Diseases Studied | Stroke, dementia, and late-life depression. |
| Significance of Findings | Modifying any one of the risk factors can reduce the incidence of the diseases. |
| Key Modifiable Factors | Blood pressure, kidney disease, diet, physical activity, and social engagement. |
| Research Institution | Mass General Brigham, affiliated with Harvard. |
| Future Directions | Call for randomized controlled trials using the Brain Care Score. |
Summary
Age-related brain diseases encompass a range of conditions, including stroke, dementia, and late-life depression, that impact older adults significantly. Recent research has revealed 17 modifiable risk factors that can help reduce the likelihood of developing these conditions. By focusing on lifestyle changes such as managing blood pressure, improving diet, and increasing physical activity, individuals can take proactive steps towards preserving brain health. Understanding these interconnected risk factors not only informs preventative measures but also emphasizes the simplicity in reducing risks associated with age-related brain diseases. Therefore, adopting healthier behaviors could lead to significant improvements in quality of life for the aging population.