Suicide prevention for older adults is an urgent issue that demands our attention as studies reveal alarming trends among this vulnerable population. Particularly for seniors aged 75 and older, the risk of suicide is the highest compared to any other age group, yet resources specifically aimed at them are grossly inadequate. Despite the increasing use of online mental health resources by older adults, national suicide prevention organizations often overlook their unique needs, leaving many without crucial support. Mental health support for the elderly is vital to combat rising geriatric suicide rates, and raising suicide awareness for seniors could significantly impact these distressing statistics. By ensuring that comprehensive and accessible resources for aging adults are developed and promoted, we can work toward mitigating this critical public health crisis.
The rising incidence of self-harm among seniors highlights the critical need for effective interventions tailored to older individuals. As we explore elder suicide prevention strategies, it becomes clear that entrepreneurs, healthcare professionals, and advocates must collaborate to enhance existing mental health resources aimed at this demographic. Social isolation and lack of awareness about available support often exacerbate the struggles faced by older adults, making it essential to spread knowledge regarding available assistance. Strategies must not only focus on direct prevention, but also aim to create a supportive community where seniors can seek help without stigma. Fostering an environment that promotes mental wellness will contribute significantly to reducing the alarming rates of suicide in the geriatric population.
Understanding the High Suicide Rates Among Older Adults
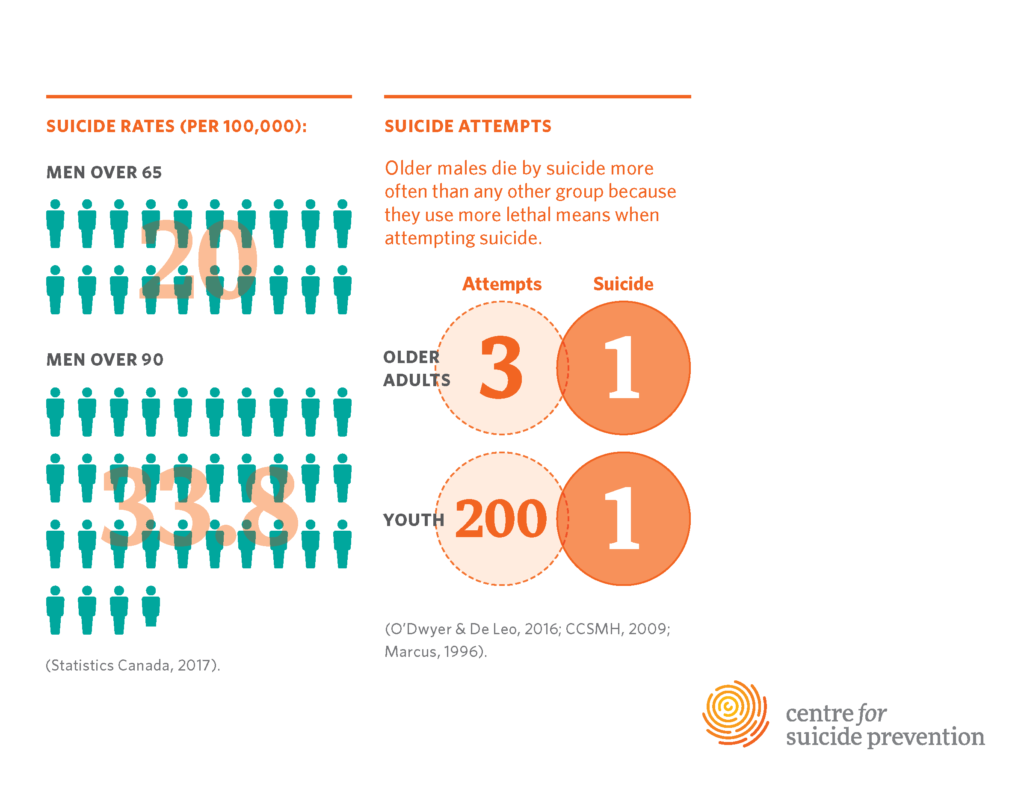
Older adults, particularly those aged 75 and older, are at an unprecedented risk for suicide, revealing concerning statistics. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), this age group experiences a staggering rate of 20.3 suicides per 100,000 individuals. This alarming figure has persisted even as many younger demographics have seen a decline in their suicide rates, underscoring a critical need for targeted intervention. Factors contributing to this disturbing trend include social isolation, loneliness, and inadequate access to mental health support for elderly individuals. As populations age globally, recognizing these challenges becomes paramount to public health.
The increasing recognition of suicide awareness for seniors is essential in addressing this issue. The imbalance in resources aimed at older adults means that many are left without the support needed to combat feelings of despair. Unfortunately, many well-known national suicide prevention organizations do not prioritize this group’s unique healthcare needs. It is crucial that these organizations revise their strategies to include older adults in their outreach efforts, thereby helping to bridge the gap between at-risk seniors and the mental health support they so desperately need.
The Urgent Need for Tailored Suicide Prevention Resources
Despite the high rates of suicide among elderly populations, there is a notable scarcity of tailored resources dedicated to their needs. A recent study highlights how online resources provided by notable organizations are often challenging for older adults to navigate. Many community members may not be aware of the specific mental health support for elderly populations available to them, leading to a detrimental silence regarding their struggles. Efforts must be made to create accessible platforms that allow these older individuals to engage with mental health resources effectively.
Additionally, developing thoroughly researched and accessible online mental health resources can empower seniors to seek help confidently. The call for increased funding to enhance geriatric suicide prevention programs is urgent. Incorporating input from older adults concerning their specific needs will enhance the effectiveness of these resources. By equipping older adults with the tools they need—whether through informative websites or community outreach programs—we pave the way for healthier outcomes in an often overlooked demographic.
Impact of Social Factors on Senior Mental Health
Social determinants greatly influence the mental health of older adults. As many face retirement, physical health issues, and the loss of loved ones, feelings of isolation can take root, exacerbating mental health challenges. These elements contribute not only to emotional distress but also to higher geriatric suicide rates, as the absence of social support networks renders individuals increasingly vulnerable. In rural areas and communities with limited access to healthcare, this issue can be particularly acute, leaving many older adults without necessary help.
To combat these adverse effects, community-based programs that promote social interaction among older adults are critical. Supporting initiatives aimed at enhancing peer connections and providing avenues for older individuals to share their experiences can mitigate feelings of loneliness. Through organized activities or workshops, these seniors can foster a support system that may protect against suicidal thoughts and behaviors, ultimately enhancing their overall mental health.
Online Resources and Their Accessibility for Aging Adults
The rise of technology has transformed the way individuals seek health information, but older adults often struggle to navigate these online resources. The lack of intuitive designs and age-friendly language can hinder their ability to access crucial information during moments of crisis. Therefore, adapting these platforms to better serve aging populations is essential in bridging the accessibility gap. Users should encounter straightforward interfaces with clearly signposted resources regarding suicide prevention that cater specifically to their age group.
Moreover, the integration of educational components about mental health—especially suicide awareness for seniors—within these platforms can foster a proactive approach to mental well-being among older adults. Increasing awareness that suicide prevention strategies exist and are accessible can encourage individuals to seek help sooner. Improving digital literacy among seniors could empower them, enabling their independent navigation of resources available to support their mental health needs.
Community Initiatives to Support Elderly Suicide Prevention
Community initiatives play a vital role in suicide prevention efforts for older adults. Engaging local organizations to create supportive environments can significantly impact the mental health landscape for this demographic. Programs designed to facilitate social engagement or provide access to mental health resources can form protective layers against the prevalent issues of loneliness and despair. Collaboration with local libraries, community centers, and healthcare providers can elevate these initiatives to reach those in need effectively.
Furthermore, integrating training programs for community volunteers and healthcare professionals on recognizing the signs of suicidal behavior in older adults can lead to timely interventions. These grassroots movements not only build awareness but also foster dialogue around mental health—all crucial steps in creating a culture that values and protects the mental health of its aging citizens.
The Role of Family in Preventing Elderly Suicide
Family support is crucial in the fight against suicidal tendencies among older adults. A strong family connection can provide emotional stability and a sense of belonging that is vital for mental well-being. When families engage in open discussions about mental health, they help to dismantle stigmas and encourage vulnerable family members to share their feelings and seek help. It is important for family members to be educated about the nuances of mental health support for elderly relatives, so they can provide appropriate resources when needed.
Creating a family environment where seniors feel comfortable discussing their mental health can significantly reduce the risk of isolation and suicidal ideation. Open lines of communication and regular check-ins can foster a supportive atmosphere that emphasizes the importance of mental well-being. Encouraging older adults to express their feelings, while also being aware of geriatric suicide rates, can help families to implement proactive measures to maintain their loved one’s mental health.
Building Awareness Through Educational Outreach
Educational outreach is essential in raising awareness about the mental health crisis facing older adults. By conducting seminars and workshops targeted at both seniors and their families, we can cultivate knowledge regarding the risks associated with suicide and the types of resources available to them. Tailoring these educational initiatives to address the unique life experiences of older adults makes the information more accessible and relatable.
Moreover, leveraging social media platforms and community newsletters can widen the reach of these programs, ensuring that information about mental health support for elderly individuals is readily available. As awareness spreads, more seniors and their families may recognize the signs of distress and reach out for help, significantly changing the narrative around elderly mental health and suicide prevention.
Innovative Strategies for Online Support Systems
As technology advances, so too should the strategies employed to aid older adults seeking mental health support. Innovative online platforms specifically designed for seniors can enhance interaction and community building. Utilizing telehealth services could provide immediate access to mental health professionals while maintaining privacy and convenience. Additionally, offering online support groups could cultivate virtual connections among older adults, promoting peer support and shared experiences.
These online mental health resources not only increase access but also allow seniors to engage at their own pace, a crucial aspect of effective therapeutic interventions. By harnessing technology to promote mental wellness, we can create a nurturing digital landscape that acknowledges and addresses the specific needs of older populations, a necessary step toward reducing geriatric suicide rates.
The Future of Research in Geriatric Suicide Prevention
Continued research focused on geriatric suicide prevention is critical in adapting effective strategies to address this urgent issue. Investigators must explore the multifaceted reasons behind the rising suicide rates among older adults, examining both psychological and sociocultural factors. By understanding the underlying causes, researchers can develop tailored prevention programs that directly address these unique challenges.
Funding for targeted studies on older adults’ mental health will enhance the breadth and depth of available interventions. Collaborations between universities, healthcare institutions, and community organizations will be vital to create a robust framework for investigating successful preventative strategies. The findings can then inform policy and lead to the implementation of resources that adequately support aging adults in navigating mental health challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most effective resources for suicide prevention for older adults?
Resources for aging adults seeking suicide prevention include local mental health services, hotlines specifically for seniors, and online mental health resources that cater to this demographic. Organizations like the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) provide useful information tailored for older adults.
How can families support their elderly loved ones in suicide prevention for older adults?
Families can play a crucial role in suicide prevention for older adults by maintaining open lines of communication, encouraging engagement in social activities, and being aware of mental health support for the elderly. Regular check-ins can help identify any signs of distress or loneliness.
What is the relationship between social isolation and suicide rates among elderly individuals?
Social isolation significantly contributes to higher geriatric suicide rates, particularly among those aged 75 and older. Loneliness can intensify feelings of despair, highlighting the importance of community engagement and support in suicide awareness for seniors.
What should I do if I suspect an elderly person is at risk of suicide?
If you suspect an older adult is at risk for suicide, it’s crucial to encourage them to seek immediate mental health support. Reach out to local mental health professionals, utilize hotlines, or explore online mental health resources tailored for older adults.
Why is there a lack of online mental health resources focused on suicide prevention for older adults?
The study indicates that many national suicide prevention organizations overlook the unique needs of older adults, leading to a deficit in easily accessible online mental health resources. This gap underscores the urgent need for targeted communication strategies aimed at seniors.
What mental health support options are available for elderly individuals experiencing suicidal thoughts?
Older adults can access various mental health support options, including counseling services, suicide prevention hotlines for seniors, and online platforms that offer tailored resources. Connecting with geriatric psychiatrists can also provide specialized care.
How do systemic biases affect suicide prevention efforts for older adults?
Systemic biases can result in underrepresentation of older adults in mental health research and programs. This often leads to a lack of tailored approaches in suicide prevention for older adults, emphasizing the need for advocacy and more inclusive strategies.
What are the signs of suicidal ideation in older adults that caregivers should look for?
Caregivers should watch for changes in behavior such as withdrawal from social activities, expressing feelings of hopelessness, changes in appetite or sleep patterns, and talking about feeling like a burden, as these may be signs of suicidal ideation in older adults.
What initiatives are being developed for suicide prevention in seniors?
Current initiatives aimed at suicide prevention for older adults focus on early intervention, accessing online mental health resources, and raising awareness about mental health support for the elderly community. Increased funding and tailored campaigns are also being advocated.
How can communities improve suicide awareness for seniors?
Communities can enhance suicide awareness for seniors by hosting educational workshops, creating support groups, partnering with local organizations, and ensuring accessible mental health resources that specifically cater to older adults.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Older Adults at Risk | Adults aged 75 and older have the highest suicide rates of any age group. |
| Lack of Resources | National suicide prevention organizations provide few resources targeting older adults, making it difficult for them to find help. |
| Imbalance in Online Efforts | Research shows online resources are predominantly aimed at younger demographics, neglecting the needs of older adults. |
| Public Awareness Needed | Campaigns targeting older adults could reduce suicide rates among this demographic. |
| Call for More Research | Increased funding and research are necessary to develop effective suicide prevention strategies for older adults. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical issue, especially considering that those aged 75 and above face the highest rates of suicide among all age groups. It is imperative that national health organizations recognize the distinct challenges this demographic faces and provide accessible, targeted resources to address their unique mental health needs. Increasing public awareness and funding for tailored prevention campaigns can effectively mitigate these alarming rates and help older adults find the support they require.